In Excel 2011 for mac, a PivotTable is a special kind of table that summarizes data from a table, data range, or database external to the workbook. If you’re PivotTable aficionado, you will be in seventh heaven with the new PivotTable capabilities in Office 2011 for Mac. Here’s how to make a PivotTable:
Excel Formula Training. Formulas are the key to getting things done in Excel. In this accelerated training, you'll learn how to use formulas to manipulate text, work with dates and times, lookup values with VLOOKUP and INDEX & MATCH, count and sum with criteria, dynamically rank. Using the Excel app, just take a picture of a printed data table on your Android or iPhone device and automatically convert the picture into a fully editable table in Excel. This new image recognition functionality eliminates the need to manually enter hard copy data. Excel tables automatically have filtering buttons for each column. Again, this is a feature that makes using Excel tables worthwhile. You can add filtering without using tables, sure—but with so many features, it makes sense to convert to tables instead. How to Quickly Apply Subtotals.
Tables In Excel For Mac
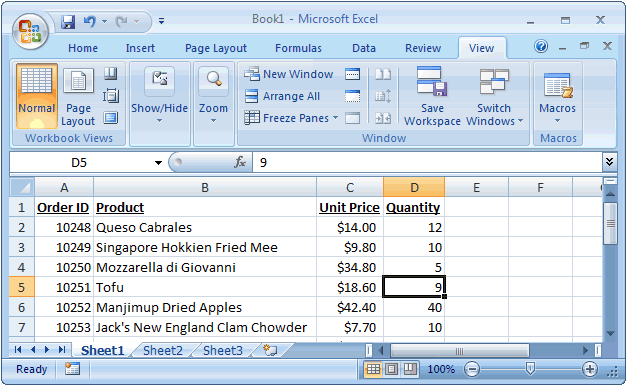
(Optional) Select a cell in your data range or table.
Choose Data→PivotTable. Alternatively, on the Ribbon’s Tables tab, go to the Tools group and click Summarize with PivotTable.
Choose the data to analyze:
Make choices from the following options:
Location: If you performed Step 1, your table or range is already filled in for you. If you didn’t start with a table or range, you can select a data range or table using the mouse.
Use an External Data Source:Displays the Mac OS X ODBC dialog.
Choose where to put the PivotTable:
New Worksheet: If selected, adds a new sheet to the workbook and places your PivotTable in Cell A1 of the new worksheet.
Existing Worksheet:Choose a cell on your worksheet. The cell will be the upper-leftmost corner of your PivotTable. Make sure there’s enough room so your PivotTable doesn’t overlap existing cell ranges.
Click OK.
Drag field names from the Field Name section at the top to the panes below.
Selecting and deselecting the field names includes or excludes the columns from the pivot table.
Clicking the pop-up buttons within the pivot table displays Filter dialogs appropriate for the data type in your pivot table.
You can filter the Field Name list by typing field names in the search box in the Pivot Table Builder dialog.
Drag fields from one pane to another to generate new pivot table variations.
You can change the column names, calculations, and number formats provided by the PivotTable Builder. There’s a little information button at the right end of each field name in the panels at the bottom of the PivotTable Builder. Click the information button to display the PivotTable Field dialog. The properties displayed are for the field name of the button you clicked:
Field Name (Optional): Type a new field name.
Summarize By: Choose which type of calculation to use.
Show Data As: Select how you want to show the data from the pop-up menu. You can choose from Normal, Difference From, % Of, % Difference From, Running Total In, % of Row, % of Column, % of Total, or Index.
Base Field and Base Item: If you choose Difference Fromin the Show Data As pop-up menu, choose which fields you’re comparing.
Delete: Removes this field from the PivotTable report.
Number: Displays the Number tab of the Format Cells dialog so you can choose a number format or make a custom number format.
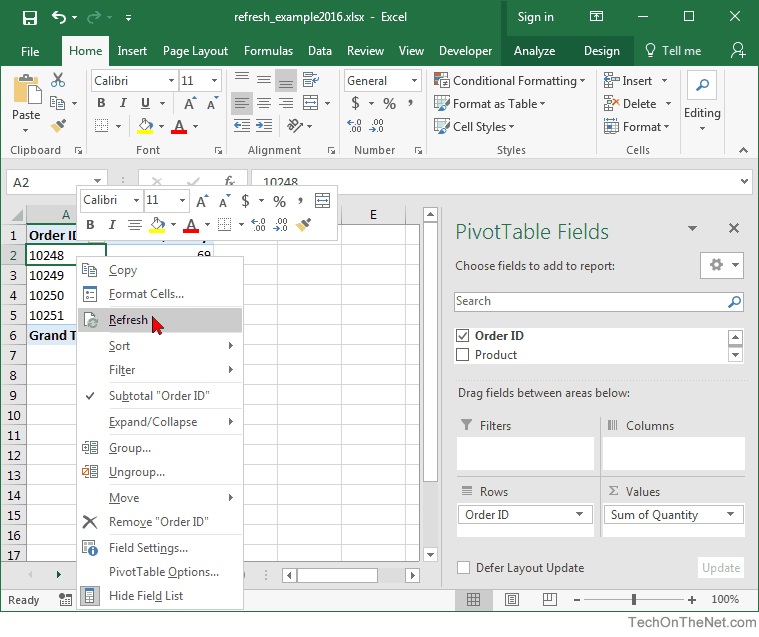
When you select a cell in a PivotTable, look at the Ribbon to find the PivotTable tab, which you click to display all sorts of PivotTable tools. The PivotTable tab is for experts. PivotTable Ribbon offers additional formatting options and still more controls for your PivotTable, but it goes beyond the scope of this book. If you find PivotTables to be useful, then by all means explore the PivotTable Ribbon.
Microsoft Excel For Mac Free
Excel 2019 makes it simple to create a new pivot table using a data list selected in your worksheet with its Quick Analysis tool. To preview various types of pivot tables that Excel can create for you on the spot using the entries in a data list that you have open in an Excel worksheet, simply follow these steps:
- Select all the data (including the column headings) in your data list as a cell range in the worksheet.
If you’ve assigned a range name to the data list, you can select the column headings and all the data records in one operation simply by choosing the data list’s name from the Name box drop-down menu.
- Click the Quick Analysis tool that appears right below the lower-right corner of the current cell selection.
Doing this opens the palette of Quick Analysis options with the initial Formatting tab selected and its various conditional formatting options displayed. - Click the Tables tab at the top of the Quick Analysis options palette.
Excel selects the Tables tab and displays its Table and PivotTable option buttons. The Table button previews how the selected data would appear formatted as a table. The other PivotTable buttons preview the various types of pivot tables that can be created from the selected data. - To preview each pivot table that Excel 2019 can create for your data, highlight its PivotTable button in the Quick Analysis palette.
As you highlight each PivotTable button in the options palette, Excel’s Live Preview feature displays a thumbnail of a pivot table that can be created using your table data. This thumbnail appears above the Quick Analysis options palette for as long as the mouse or Touch pointer is over its corresponding button. - When a preview of the pivot table you want to create appears, click its button in the Quick Analysis options palette to create it.
Excel 2019 then creates the previewed pivot table on a new worksheet that is inserted at the beginning of the current workbook. This new worksheet containing the pivot table is active so that you can immediately rename and relocate the sheet as well as edit the new pivot table, if you wish.
The following figures show you how this procedure works. In the first figure, the fourth suggested PivotTable button in the Quick Analysis tool’s option palette is highlighted. The previewed table in the thumbnail displayed above the palette shows the salaries subtotals and grand totals in the Employee Data list organized whether or not the employees participate in profit sharing (Yes or No).
Excel Pivot Tables For Mac
The second figure shows you the pivot table that Excel created when I clicked the highlighted button in the options palette in the preceding figure. Note this pivot table is selected on its own worksheet (Sheet1) that’s been inserted in front of the Employee Data worksheet. Because the new pivot table is selected, the PivotTable Fields task pane is displayed on the right side of the Excel worksheet window and the PivotTable Tools context tab is displayed on the Ribbon. You can use the options on this task pane and contextual tab to then customize your new pivot table.
Excel And Word For Mac
Note that if Excel can’t suggest various pivot tables to create from the selected data in the worksheet, a single Blank PivotTable button is displayed after the Table button in the Quick Analysis tool’s options on the Tables tab. You can select this button to manually create a new pivot table for the data.