I recommend you to use the latest version of Qt (5.10 at the moment) and Qt Creator (4.5.0 at the moment), because some annoying Android-related issues were fixed there, and thus everything is easier now. The process is more or less the same across all the major development hosts (Linux, Mac OS. Qt Quick Positioning and explore subjects like Anchors, Positioners, Layouts and Flow. Qt Quick on Mobile Devices: we take you on a detailed journey on how to run your Qt Quick Apps on Android and guide you on how you would do the same on IoS. Qt binding for Go (Golang) with support for Windows / macOS / Linux / FreeBSD / Android / iOS / Sailfish OS / Raspberry Pi / AsteroidOS / Ubuntu Touch / JavaScript / WebAssembly - therecipe/qt.
If you are a network administrator, you probably have to deal with mac addresses often. MAC address is required to identify a device on a particular network and manage its connection. Although it’s similar to the device ID, but it’s specifically used for network connection.
You can use it to restrict network access to specific devices, apply network rules, and even change it to spoof a different device. I am sure you can see how important it is to know your device’s MAC address. Therefore, today I will show you 4 ways to find MAC address on any Android phone.
1. Find MAC address from the device information
The quickest way to find MAC address on Android is to look for it in the About device section.
Here’s how to access it:
- Go to “Settings” and tap on “About device”.
- Here tap on “Status” and you’ll find the MAC address under the “WiFi MAC address”
You can tap and hold on the MAC address to copy it and paste it anywhere you like.
2. Find MAC address from the WiFi settings
Alternatively, you can also find MAC address from WiFi advanced settings. Follow the below instructions:
- Access “Settings” and tap on “Connections” (or WiFi and networks) option.
- Now tap on “Advanced” button at the top-right corner.
- In the Advanced settings, you’ll find the MAC address at the bottom.
3. Use a dialer code to find MAC Address
If you are one of those geeky users who like using codes, then you’ll surely like this option. Like many other secret Android codes, there is also a dial pad code to find MAC address on Android. Here’s is what you need to do:
Open up the dial pad (the app you use for calling) and enter the code *#*#232338#*#*. A tiny window will open up to show your mac address.
Note: This trick may not work on some Android phones. For example, it doesn’t work on my Samsung device.
4. Use a MAC address finder app
Qt Android Mac Os X
If you frequently need to look for the MAC address of your Android phone, then using a dedicated app might be a better option. There are many apps for this purpose, but I recommend What’s my MAC address for its simplicity.
Just install and launch the app and it will show the device MAC address on the top. Additionally, it also shows SSID and BSSID (WiFi MAC address), which could also be useful in many situations. If you need to copy any of the information, just tap and hold on it.
Ending thoughts
These are all the methods I know to find MAC address on Android devices. I particularly like the first method on this list as it’s easier to access and you also have the option to copy the MAC address. If you know any other ways to find MAC address on Android, let us know in the comments below.
Android is one of the Qt’s supported target platforms, so you can create applications for Android using Qt.
Here I’ll show you how to set-up Qt development environment for Android.
Actually, the process is already described in the Qt documentation: setting up both the environment and Qt Creator. However (as usual), there are some surprises that are waiting for you down the road, so I decided to complement the official guide with my comments and screenshots.
I recommend you to use the latest version of Qt (5.10 at the moment) and Qt Creator (4.5.0 at the moment), because some annoying Android-related issues were fixed there, and thus everything is easier now.
The process is more or less the same across all the major development hosts (Linux, Mac OS, Windows). I’ll do it for Linux (running inside a virtual machine on my Mac).
First, install Android component from the Qt installer:
I have here HTC Evo 3D (Android 4.0.3), Google Nexus 7 (Android 6.0.1), and Google Pixel C (Android 8.1.0):
…so I chose Android ARMv7.
Download and install Android Studio. I unpacked it to ~/programs/android-studio/. Now run ~/programs/android-studio/bin/studio.sh. It will ask you for an installation path (I chose ~/programs/android/) and then install Android SDK and Android SDK Platform (latest version by default).
If you want to check what’s installed, launch Android Studio again and go to settings:
Here’s what I have:
On Windows you will also need to install Google USB driver:
Now download and unpack Android NDK. I put mine to ~/programs/android-ndk/. Note that at the moment (Qt Creator 4.7.1 and Qt 5.11.1) NDK version r18 won’t work, you should take 17c.
Download and unpack JDK. At the moment there are some problems with JDK 9, so it is recommended to go with JDK 8. I put mine to ~/programs/jdk/.
Check if you have some not accepted licenses:
You might get this error:
I tried adding JAVA_HOME to environment variables, but it didn’t make any difference, so I simply added path to JRE (~/programs/jdk/jre/bin) to the PATH variable.
Run it again:
and accept the licenses:
If you won’t accept all the licenses, something simply might not work.
So, here are all my paths:
- Android Studio:
~/programs/android-studio/(although, this path is not needed); - Android SDK:
~/programs/android/; - Android NDK:
~/programs/android-ndk/; - JDK:
~/programs/jdk/.
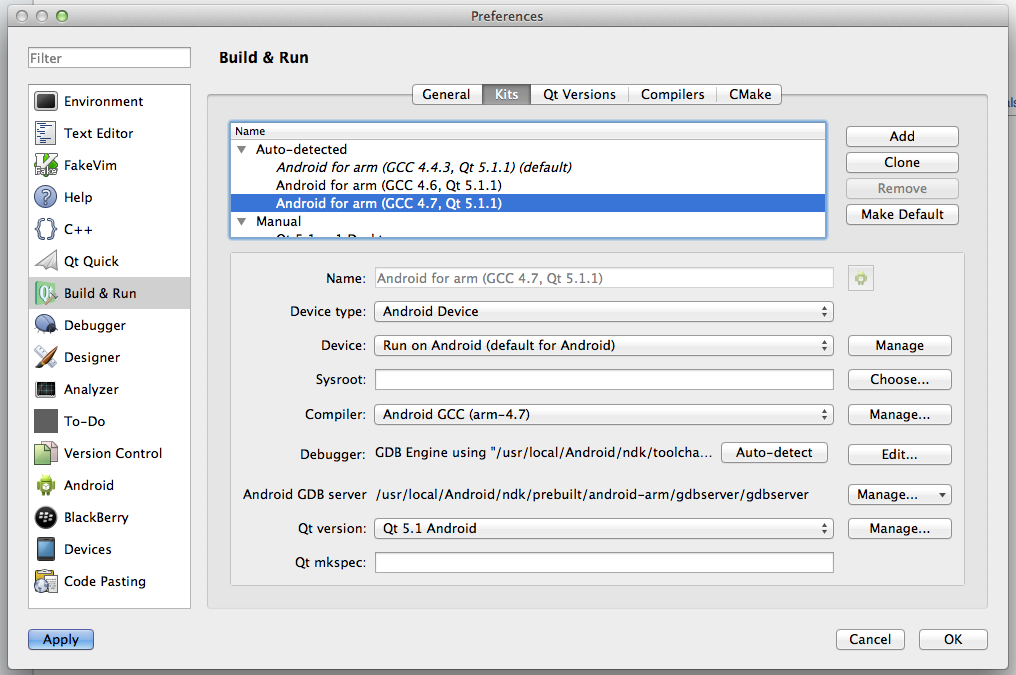
And now you can launch Qt Creator and set them all at the Android tab:
If something is wrong, it will offer you to download missing components:
And if you installed JDK 9, it will fail. I warned you.
If you don’t have Android tab in the Qt Creator settings, check if you have Android plugin enabled:
This part is done.
Now enable Developer mode (and USB debugging) on your Android device and connect it to your PC. You can check the connection by running:
I connected all 3 devices, so here’s my output:
On Linux you might see something like this, though:
On Windows it will be just:
Or, which is more confusing, you might get ABI is incompatible error while trying to deploy your application:
Both issues (no permissions/unauthorized and incompatible ABI) most probably indicate that you didn’t allow your PC to debug your Android device via USB. It’s not necessarily your fault, especially if you (like me) never got this request in the first place. In order for your Android device to show you debugging request, you need to restart ADB daemon (while your device is connected to the PC):
Now you should get a dialog like this on your device:
Qt For Android Mac Download
Information from this page also tells to install Android adb tools package. I’m not sure how much use does it bring since we already have it from Android Studio, but okay:
Anyway, once you allow the debugging request, your device will be recognized by ADB (and Qt Creator deployment dialog).
Time to build and run some application on your Android device. I will use the Color Corners example again, which is not an Android application by design, but it’s a cross-platform framework we are dealing here with, so why the hell not.
If everything was set-up correctly, you should be able to see the Android build SDK version in your project build settings:
You can also add Android manifest and other templates:
That will allow you to specify the application name, icon, permissions and other stuff (but don’t use spaces, otherwise your application will fail to launch saying that it couldn’t find a library):
Now you can just run your application from Qt Creator:
And here we say “sorry” to HTC Evo 3D, because it has a really old Android API (15):
Qt For Android Mac Usb
So we’ll launch our application only on Nexus 7 and Pixel C targets:
Qt For Android Cannot Find -lc
As you can see, our application was successfully built for Android platform, so it is an .apk file, which can be either run on the connected device from Qt Creator, or you can copy it to the device manually and install it there.